

Ankle sprain is injury of ankle, happens when it rolls, turn or twist awkwardly. Various other injuries also mimic ankle sprain. Most of the time these injuries are ignored and cause long term morbidity.
Ankle joint consist of three bone Tibia on top and inner aspect, fibula on lateral aspect creating a hinge holding the dome of talus below. It is a fluid containing joint allowing only upwards and downwards movement. There are few ligaments around the joint which hold all the bone together and maintains the integrity of the joint. The whole foot moves around the ankle joint in upward and downward direction. Heel below ankle joint can move in inward and outward angulation. Both the ankle and heel movement together keep the foot flexible and adjust the alignment with lower limb while walking and landing on different plane. Following picture demonstrate the important ligaments of the ankle joint. The outer side ligaments are more prone to injury during ankle sprain.
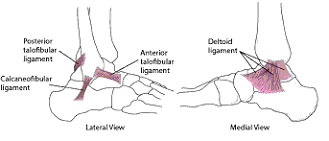
Inward heel movement is more than outward heel movement. While walking on uneven surface or during landing if the heel moves more away from the vertical weight bearing axis of body then the body weight forces it to move further beyond the capacity of the ligaments and fibres of the ligaments may get stretched or torn. Common affected ligaments are ligaments attaching fibula bone to talus and calcaneum. Less common affected ligaments are, ligament holding tibia and fibula, calcaneum and cuboid. Other than ligament tendon and bones on outer aspect of the ankle and foot can also get injured, like peroneal tendon, anterior process of calcaneum, base of 5th metatarsal. Same mechanism of injury can also result in ankle fracture depending on the force affecting the injury.
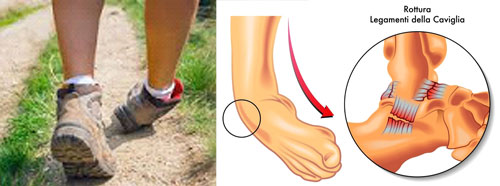
Mechanism of ankle injury and ligaments affect
There are few factors which increases the probability of ankle sprain like,
One usually feels a pop sound at the time of sprain followed by severe pain and inability to walk and stand. Gradually develops swelling and ecchymosis. X-ray not required most of the ankle sprain. But if there is tenderness directly over bony prominence and is more than that of tissue area or in very high-grade sprain X-ray is required. Sometimes MRI is also of great help.
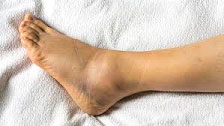
Condition of ankle following sprain
Most of the ankle injuries heals completely without any residual morbidity but there can be residual long-term morbidity following ankle sprain,
Rest, icepack, compression and elevation (RICE) is the key treatment of all ankle sprain which can start even before visiting a specialist. It needs restriction of ankle movement and support for 2 weeks followed by mobilization and physical rehabilitation. Physical rehabilitation involves relieve off stiffness, strengthening of muscle around ankle and regaining proprioception. All ankle sprained should be reviewed for other injuries and aftereffect if there is lingering symptom beyond 6 -12 weeks. Very few ankle sprains may need surgical intervention. Following are the different surgical treatment of ankle sprain